The Connection Between Autoimmune Disease and Dental Health
Understanding the Autoimmune Disease that Affects the Teeth | Boise Emergency Dentist
Autoimmune diseases are a group of disorders that affect the body's ability to recognize its own cells and tissues, resulting in an immune response against them. This can lead to tissue damage, inflammation, organ failure, and other serious issues.
One such autoimmune disease is one that affects the teeth; this article will explore what this condition is and how it should be managed. Autoimmune diseases affecting the teeth can cause pain and discomfort for individuals who suffer from them. They may also result in further dental problems due to their effect on the soft and hard tissues of the mouth.
It is important for those affected by these conditions to understand both the signs and symptoms associated with them as well as the potential treatments available, so they can seek appropriate care when needed. For more information,
contact Emergency Dental Boise with your inquiries.
What Is Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth?
Autoimmune disease is a complex condition where the body’s own immune system mistakenly attacks its own healthy tissues, resulting in inflammation and other potentially serious health issues.
In some cases, it can affect the teeth, leading to oral hygiene concerns. While autoimmune triggers are not yet fully understood, there are certain factors that may contribute to the development of this type of illness.
A number of diseases have been identified as being caused by an overactive immune system attacking self-tissues; these include rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), psoriasis, and multiple sclerosis (MS).
In addition to these common conditions, autoimmune disease can also cause various dental problems such as gingivitis, periodontal disease, or alveolar bone loss. Studies have shown that people with certain autoimmune disorders are more likely to experience tooth decay due to reduced saliva flow or altered salivary composition, which can lead to bacterial growth on the teeth's surface, causing cavities.
In order to reduce the risk of damage from autoimmune diseases affecting teeth, preventative measures should be taken, including proper brushing and flossing techniques along with regular visits to the dentist for
professional dental cleaning. Additionally, controlling any underlying medical conditions through lifestyle changes or medications may help alleviate symptoms associated with autoimmunity and improve overall dental health. Taking care of one's oral hygiene is essential for maintaining good overall health and keeping potential complications at bay.
Signs And Symptoms Of Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth
Autoimmune diseases can affect the teeth in a variety of ways. The symptoms may be quite subtle, and some people do not experience any noticeable signs or symptoms at all. However, for those who do, there are certain commonalities that include:
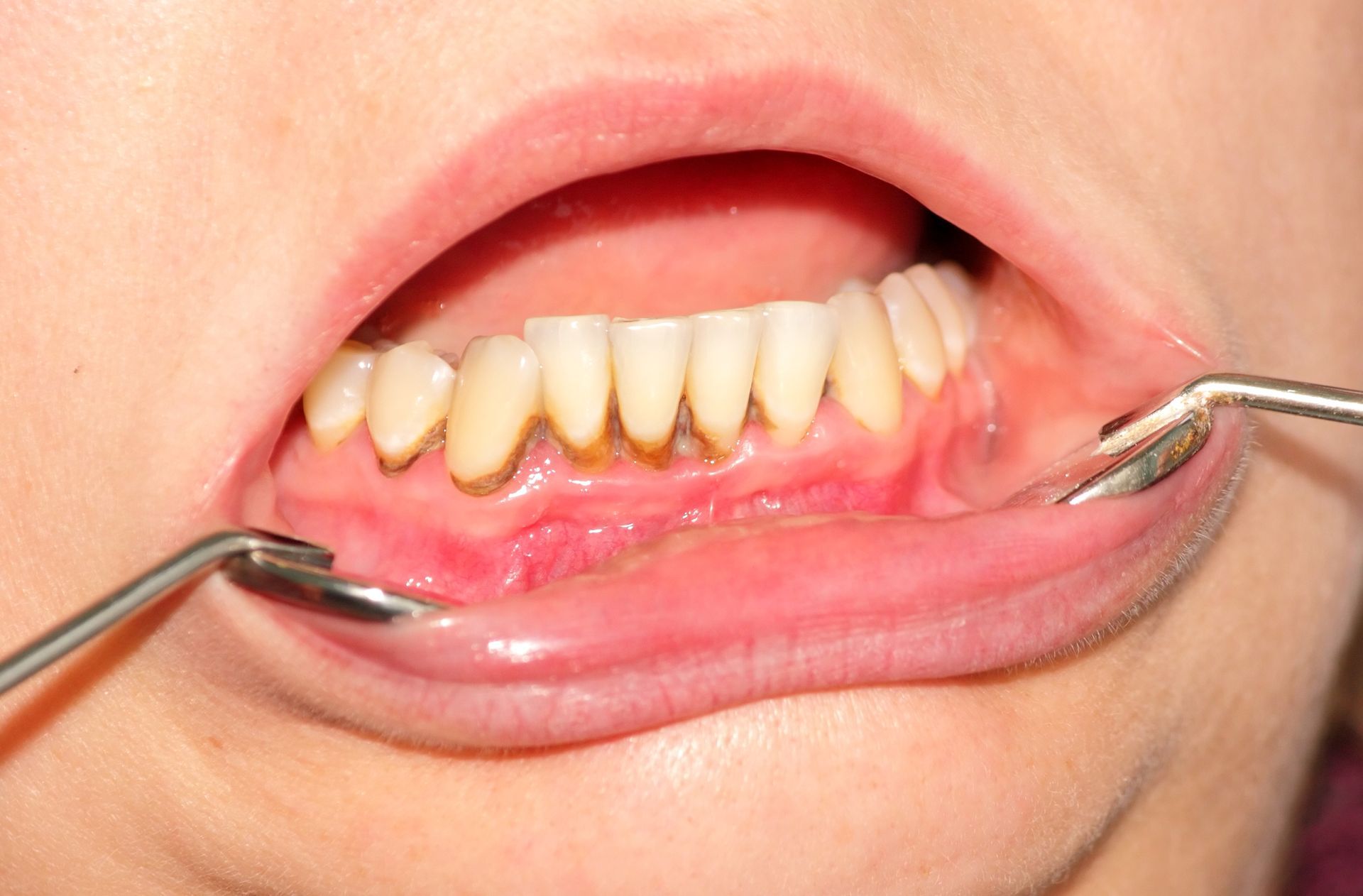
- Oral inflammation is one of the most common signs of an autoimmune condition affecting the teeth. It is characterized by redness, swelling, and/or tenderness around the gums and other parts of the mouth. In addition to oral inflammation, some individuals may also experience difficulty eating due to pain or discomfort caused by their inflamed tissues.
- Gum recession – Another sign of an autoimmune disease affecting the teeth is gum recession. This occurs when your gums pull away from your tooth roots, exposing them and making them vulnerable to infection or decay. If left untreated, it can lead to loose teeth and even further damage over time.
In severe cases, individuals with autoimmune conditions impacting their teeth may develop ulcers on their tongue or inside their cheeks, which can cause significant discomfort as well as interfere with normal daily activities such as speaking or chewing food properly. Additionally, they may find that their breath smells differently than usual because of this condition.
Treatment options vary depending on severity but typically involve controlling inflammation through medications designed specifically for autoimmunity-related issues as well as cleaning and maintaining good dental hygiene habits, including regular brushing and flossing.
Causes Of Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth
Autoimmune diseases that affect the teeth are often difficult to diagnose and manage. They can cause a myriad of symptoms, from sensitivity in the mouth to tooth discoloration. To better understand these conditions, it is important to review the causes of such illnesses as well as potential treatments.
The most common cause of an autoimmune disease affecting teeth is poor oral hygiene. Bacteria build up on the surface of teeth due to improper brushing and flossing techniques, leading to an overgrowth of harmful organisms. These bacteria then trigger an immune response, which can lead to inflammation, pain, and other dental problems.
Additionally, genetics may play a role in causing certain autoimmune disorders of the teeth. An autoimmune diet has been proposed by many experts as one way to reduce or eliminate symptoms associated with autoimmune diseases of the teeth. This type of dietary plan focuses on eliminating foods known to trigger inflammatory responses while increasing consumption of nutrient-rich whole foods and probiotics. By making small changes in what you eat, it may be possible to improve overall health and help alleviate some dental issues caused by autoimmune diseases.
Treatment For Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth
Autoimmune disease, a condition in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells and tissues, can have a major impact on oral health and hygiene. Many of these diseases cause pain, discomfort, or even destruction of teeth; therefore, it is important to recognize the symptoms and signs so that proper treatment can be administered as early as possible.
When considering conditions affecting teeth, autoimmune diseases are often overlooked by those outside the medical field. Common examples include Sjögren's syndrome, lupus-related oral ulcers (LOU), pemphigoid/Pemphigus vulgaris (PV), Behçet’s syndrome (BS), and gluten ataxia. These illnesses all share similar characteristics, such as dry mouth caused by salivary glands, resulting in poor dental health due to insufficient saliva production for natural cleansing. Other features may include redness or swelling of the gums along with painful ulcerations inside the cheeks accompanied by fever blisters around the lips.
Treatment typically consists of combination therapies tailored to each individual patient depending upon their specific needs, but generally includes good oral hygiene practices combined with stress management techniques to maintain optimal oral health.
Practicing daily brushing and flossing helps remove bacterial buildup, while using rinses containing xylitol can help reduce inflammation of the gum tissue. Additionally, maintaining low levels of stress has been proven beneficial in decreasing flareups associated with autoimmune disease related problems within the mouth.
Developing an effective treatment plan requires collaboration between patients and healthcare providers to ensure success since individuals suffering from autoimmune disorders need specialized care when dealing with their dental issues. With this approach, many people are able to successfully manage their condition through lifestyle modifications that lead them back towards healthier mouths without requiring the drastic medical interventions necessary prior to diagnosis.
Is Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth Hereditary?
Recent studies have shown that autoimmune diseases affecting the teeth may be hereditary in certain cases. However, there are also lifestyle factors such as oral hygiene and stress management that can play a role in preventing or mitigating the effects of this condition.
It is important to note that maintaining good dental health through regular brushing and flossing, avoiding sugary foods and drinks, visiting your dentist regularly for check-ups, and managing stress levels can help reduce the chances of developing an autoimmune disease affecting the teeth.
Are There Any Lifestyle Changes That Can Help Minimize Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth?
Stress relief and proper oral hygiene can help minimize autoimmune diseases affecting teeth. It is important to remember that some forms of autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), are not caused by stress, but the symptoms may be worsened by it.
Therefore, reducing stress levels with lifestyle changes, including physical activity and relaxation techniques like yoga and meditation, may prove beneficial in managing the effects of an autoimmune disorder on your teeth.
In addition, practicing good oral hygiene habits, including brushing twice a day, flossing once daily, avoiding sugary foods and drinks, and visiting the dentist regularly for checkups, will also help minimize any damage to teeth due to autoimmunity.
How Is Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth Diagnosed?
Early detection of autoimmune diseases affecting teeth is essential for successful treatment and prevention. The prevalence rate of gluten sensitivity as an underlying cause for such diseases has been estimated at 6-7%.
The diagnosis typically involves a physical examination, dental imaging, blood tests to assess inflammation levels in the body, and evaluation of any antibodies present that are related to celiac disease or other autoimmune conditions. A dentist may also order genetic testing if they suspect a patient has a rarer form of an autoimmune disorder affecting the teeth.
Engaging patients by speaking to them about their symptoms in a manner that conveys belonging caensure an ensure early diagnosis and prevent further complications from developing.
Are There Any Alternative Treatments For Autoimmune Disease Affecting Teeth?
Alternative treatments for autoimmune diseases affecting teeth can include dietary remedies, mental health strategies, and lifestyle modifications. Dietary remedies such as gluten-free diets are commonly used to alleviate symptoms of autoimmune diseases that affect the teeth.
Additionally, studies have found that supplementing with vitamins and minerals may be beneficial in some cases. Mental health interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can also help those suffering from an autoimmune disorder involving their teeth manage stress levels and reduce anxiety, which is often associated with these disorders.
Lastly, making lifestyle changes such as reducing or eliminating exposure to environmental toxins has been shown to improve overall wellbeing for individuals living with this condition.
Talk To Professional Emergency Dentist Of Boise
Autoimmune diseases affecting teeth can have long-term effects. Research suggests that one in every twenty Americans is affected by some form of autoimmune disease, which can lead to pain and inflammation in the mouth, as well as tooth decay and infection.
It is important for patients to understand their options when it comes to the diagnosis and treatment of this condition. Diagnosis methods include blood tests, x-rays, or tissue biopsies, and treatments range from lifestyle changes, such as diet modification, to traditional medications or alternative therapies.
Ultimately, proper management of an autoimmune dental condition requires a tailored approach based on each patient’s individual needs. With early detection and appropriate treatment plans, individuals with autoimmune diseases affecting teeth may be able to reduce the risk of further damage and maintain good oral health.